介绍
二叉排序树又称二叉搜索树,听名字都知道是方便排序和查找的树
定义
可以是一颗空树 或者是具有如下性质的二叉树
- 若左子树不空 则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 若右子树不空 则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 它的左右子树也都是二叉排序树
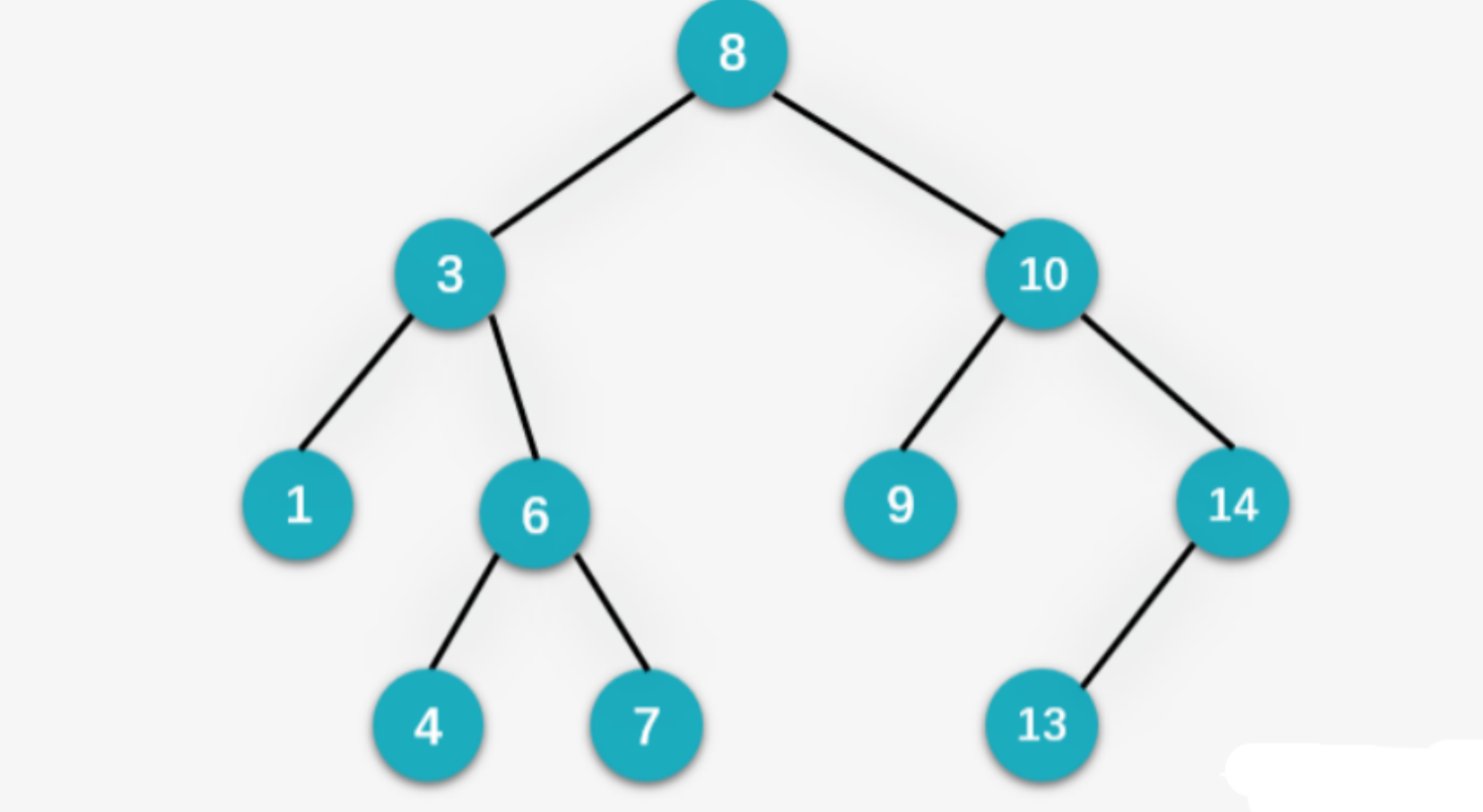
特点
中序遍历是一个有序序列,比如上图的中序遍历结果是: [1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 13, 14]
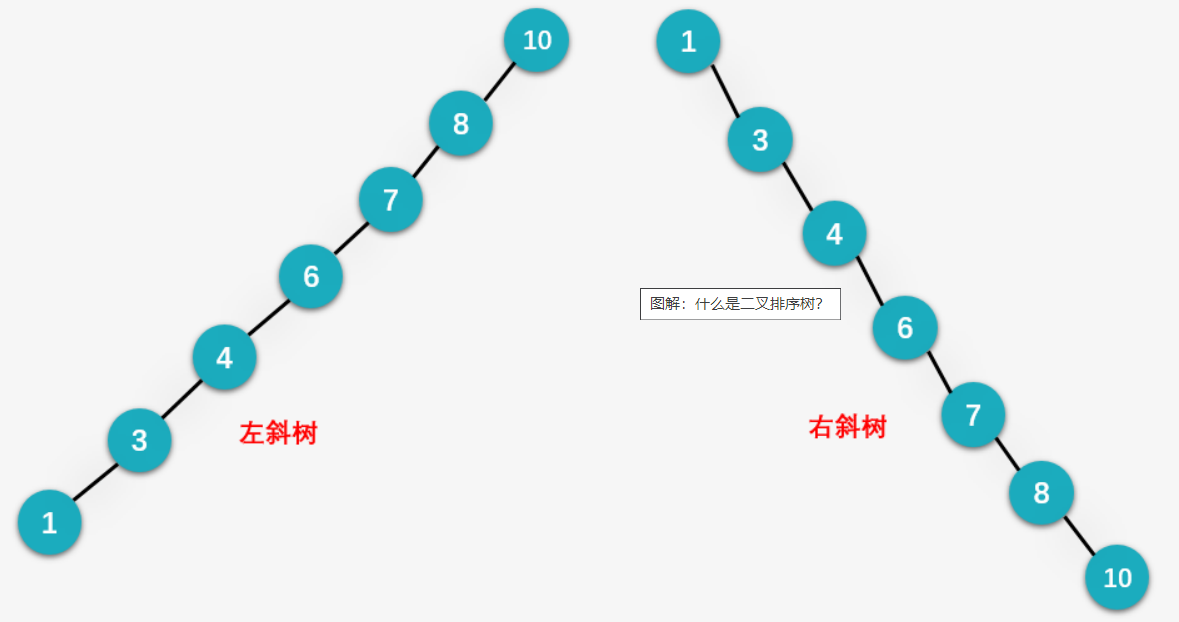
查找复杂度取决于深度,好的话是二叉树的O(logn),坏的话就是斜树的O(n)
实现
这里采用typescript实现,所以先定义好类型
export class BSTreeNode<T = number> {
val: T;
left: BSTree<T>;
right: BSTree<T>;
constructor(val: T, left?: BSTree<T>, right?: BSTree<T>) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left ? left : null;
this.right = right ? right : null;
}
}
export type BSTree<T = number> = BSTreeNode<T> | null;新增
如果新增节点的值比当前节点大,则插入到节点右边,小则插入到左边
/** 新增节点: 作为叶子节点插入 */
export function insertBSTreeNode<T>(root: BSTree<T>, val: T): BSTree<T> {
if (root === null) return new BSTreeNode(val);
if (val < root.val) {
if (root.left === null) {
root.left = new BSTreeNode(val);
} else {
insertBSTreeNode(root.left, val);
}
} else {
if (root.right === null) {
root.right = new BSTreeNode(val);
} else {
insertBSTreeNode(root.right, val);
}
}
return root;
}通过数组构建二叉排序树
其实就是遍历数组的值不断新增即可
/** 构建二叉排序树 */
export function createBSTree<T>(arr: T[]): BSTree<T> {
if (arr.length === 0 || arr[0] === null) return null;
const root = new BSTreeNode(arr[0]);
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
insertBSTreeNode(root, arr[i]);
}
return root;
}遍历二叉排序树
这里通过中序遍历 直接获得一个有序序列
/** 遍历二叉排序树: 中序遍历 */
export function traverseBSTree<T>(root: BSTree<T>): T[] {
if (root === null) return [];
const arr: T[] = [];
const left = traverseBSTree(root.left);
arr.push(...left, root.val);
const right = traverseBSTree(root.right);
return [...arr, ...right];
}查找节点
其实就是通过判断大小来查找,如果比当前节点大就在右子树查找,否则左子树查找
/** 查找节点 */
export function findBSTressNode<T>(root: BSTree<T>, val: T): BSTree<T> {
if (root === null) return null;
if (root.val === val) return root;
if (val < root.val) return findBSTressNode(root.left, val);
return findBSTressNode(root.right, val);
}一些特性方法
前驱后驱的意思是有序序列下的上一个节点和下一个节点,比如上图中8的前驱节点是7,后驱节点是9。
其中获取前后驱节点在删除方法时候需要用到
/** 获取树的最小节点 */
export function getMinBSTreeNode<T>(root: BSTree<T>): BSTree<T> {
if (root === null) return null;
if (root.left === null) return root;
return getMinBSTreeNode(root.left);
}
/** 获取树的最大节点 */
export function getMaxBSTreeNode<T>(root: BSTree<T>): BSTree<T> {
if (root === null) return null;
if (root.right === null) return root;
return getMaxBSTreeNode(root.right);
}
/** 获取前驱节点: 左子节点树的最大值 */
export function getPrevBSTreeNode<T>(root: BSTree<T>): BSTree<T> {
if (root === null) return null;
if (root.left === null) return null;
return getMaxBSTreeNode(root.left);
}
/** 获取后驱节点: 右子节点树的最小值 */
export function getNextBSTressNode<T>(root: BSTree<T>): BSTree<T> {
if (root === null) return null;
if (root.right === null) return null;
return getMinBSTreeNode(root.right);
}删除节点
这个方法也是所有方法中最复杂的,待删除节点可细分为以下情况
- 叶子节点: 直接删除
- 节点只有左子树或者右子树: 节点删除 将节点的左子树或者右子树移到删除节点的位置上
- 节点既有左子树也有右子树: 找到节点的前驱/后继节点替换该节点 并删除前驱/后继节点(递归删除)
/** 删除节点 **/
export function removeBSTreeNode<T>(root: BSTree<T>, val: T): BSTree<T> {
if (root === null) return null;
if (root.val === val) {
if (root.left === null && root.right === null) {
// 叶子节点
return null;
} else if (root.left === null) {
// 只存在右子树
return root.right;
} else if (root.right === null) {
// 只存在左子树
return root.left;
} else {
// 既存在左子树也存在右子树 这里采用寻找后继节点替换的方式
const nextNode = getNextBSTressNode(root)!;
root.val = nextNode.val; // 将后继节点的值赋值给当前节点
root.right = removeBSTreeNode(root.right, nextNode.val); // 递归删除后继节点
}
} else if (root.val > val) {
root.left = removeBSTreeNode(root.left, val);
} else {
root.right = removeBSTreeNode(root.right, val);
}
return root;
}总结
二叉排序树是一个专门为查找而诞生的树,如果构建得当是可以将查找的效率降低到O(logn)的情况,但是如果构建成斜树的情况,其实和链表就是一样的了,查找复杂度变成O(n)。