前言
瀑布流是一种布局方式,实现瀑布流有很多种方法,例如flex,grid布局,但或多或少有这样那样的问题。所以这里介绍的是最传统也是兼容性最好的方法,绝对定位布局。
实现思路
首先我们来看看瀑布流长啥样
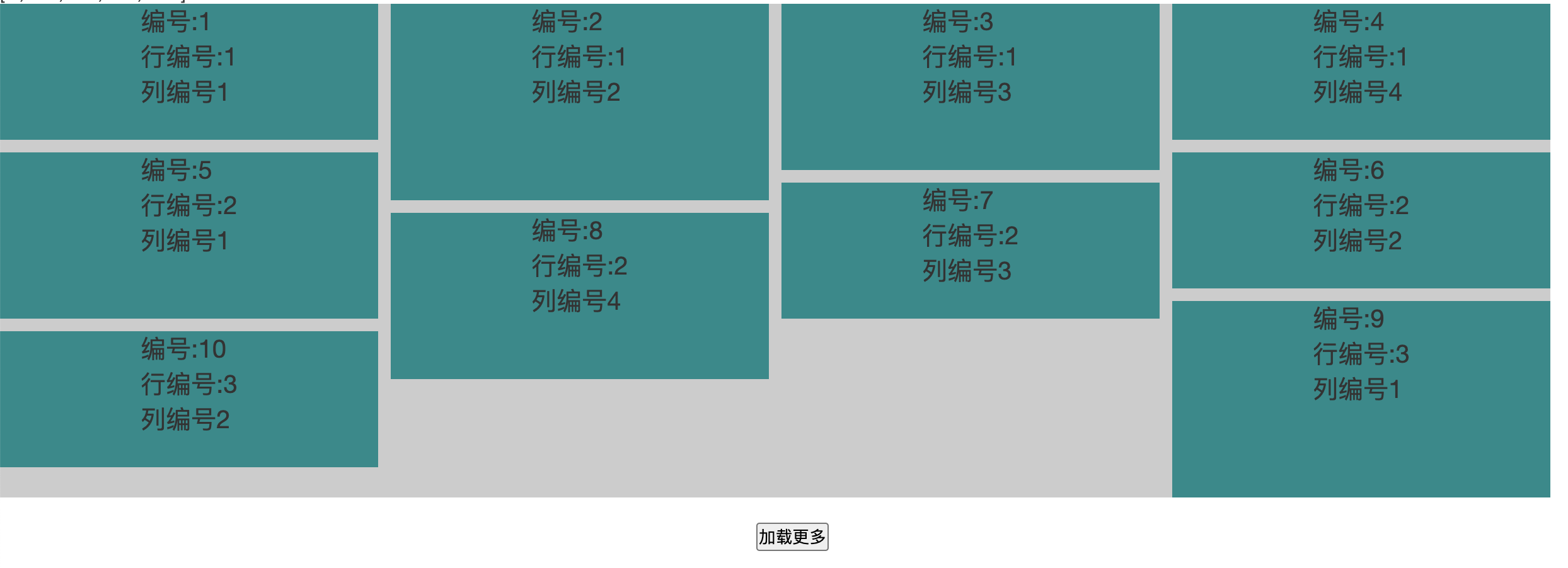
首先基于瀑布流的特点,我们很容易就能定义出这几个变量
data() {
return {
containerWidth: 1230, // 容器的长度
colCount: 4, // 每列的个数
colGap: 10, // 每列的空隙
};
}然后为了区分元素,这里给元素进行编号(从1开始),那么行编号和列编号也可以计算得出
data() {
return {
num: 1,
// 省略...
}
},
// 编号
const num = this.num++;
// 当前行编号: 从1开始
const rowNum = Math.ceil(num / this.colCount);
// 当前列编号: 从1开始
const colNum = num % this.colCount || this.colCount;瀑布流的特点就是先排满一行,但是因为元素有高有矮,所以底部显得参差不齐。在开启下一行的渲染时候,元素应该在当前高度中最短的列中进行生成,如上图所示,编号5的元素排在编号1的下面,因为当前编号1所在的列最矮,这个应该很容易理解。
那这个是怎么实现的呢,其实很简单,就是用一个数组记录当前列的高度,下次渲染元素就渲染在最矮列下面,最高列的高度则是瀑布流的整体高度。
created() {
// 初始化第0列的高度
this.currheights = new Array(this.colCount + 1).fill(0);
},
data() {
return {
// 省略...
currheights: [] // 缓存当前每列的高度
};
},
computed: {
// 当前列的最大高度
maxCurrHeight() {
return Math.max(...this.currheights);
},
// 当前最矮列的编号
minShortColNum() {
let num = 1;
for (let i = 2; i <= this.currheights.length; i++) {
if (this.currheights[num] > this.currheights[i]) {
num = i;
}
}
return num;
}
}对于渲染一个元素来说,我们需要知道的无非是width, height, top, left,因为这里介绍的是不定高度的做法,所以height是渲染完元素才能知道,这也就导致实际一个列表,我们只能一个个渲染,即拿到上一个高度,根据当前列高度再渲染下一个元素的位置。
容器长度,每列个数和间距大小都是确定的,那么width自然也是确定的,width = (容器长度 - (每列个数 - 1) * 间距) / 每列个数,这个很好理解;难点在于top和left怎么计算呢?
left其实就是当前最矮列距离左边的距离,因为我们优先填满最矮的那列嘛
const left = (this.minShortColNum - 1) * (width + this.colGap);top则需要分情况讨论,如果是第一行则为0,否则就是当前列(最矮列)的高度 + 边距。
const currColHeihgt = rowNum === 1 ? 0 : this.currheights[this.minShortColNum];
const gap = rowNum === 1 ? 0 : this.colGap;
const top = currColHeihgt + gap;完成例子
这里给出上面瀑布流截图的具体实现例子,在线访问
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, maximum-scale=1, user-scalable=no, viewport-fit=cover"
/>
<title>瀑布流-定位实现</title>
<style>
.m-list {
position: relative;
background-color: #ccc;
}
.m-item {
position: absolute;
background-color: darkcyan;
display: inline-flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
vertical-align: top;
font-size: 20px;
word-break: break-all;
}
.m-btn {
margin-top: 20px;
margin-left: 600px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{currheights}}</p>
<div class="m-list" :style="{width: `${containerWidth}px`, height: `${maxCurrHeight}px`}">
<div
class="m-item"
v-for="item in items"
:key="item.num"
:style="{width: `${item.width}px`, top: `${item.top}px`,left: `${item.left}px`}"
:ref="`item${item.num}`"
v-html="item.content"
></div>
</div>
<p class="m-btn"><button @click="requestItems">加载更多</button></p>
</div>
</body>
<script src="../lib/vue.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data() {
return {
num: 1, // 编号
pageNum: 1,
pageSize: 10, // 每次请求两行
items: [],
containerWidth: 1230, // 容器的长度
colCount: 4, // 每列的个数
colGap: 10, // 每列的空隙
currheights: [] // 缓存当前每列的高度
};
},
computed: {
// 当前列的最大高度
maxCurrHeight() {
return Math.max(...this.currheights);
},
// 当前最矮列的编号
minShortColNum() {
let num = 1;
for (let i = 2; i <= this.currheights.length; i++) {
if (this.currheights[num] > this.currheights[i]) {
num = i;
}
}
return num;
}
},
created() {
// 初始化第0列的高度
this.currheights = new Array(this.colCount + 1).fill(0);
},
mounted() {
this.requestItems();
},
methods: {
// 请求下一页数据
async requestItems() {
let list = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.pageSize; i++) {
// 编号: 从1开始
const num = this.num++;
// 当前行编号: 从1开始
const rowNum = Math.ceil(num / this.colCount);
// 当前列编号: 从1开始
const colNum = num % this.colCount || this.colCount;
// 长度: (总长度-间隔长度)/列数
const width = (this.containerWidth - (this.colCount - 1) * this.colGap) / this.colCount;
// top: 当前行+间隔 (第一行不需要上一行的高度和间隔)
const currColHeihgt = rowNum === 1 ? 0 : this.currheights[this.minShortColNum];
const gap = rowNum === 1 ? 0 : this.colGap;
const top = currColHeihgt + gap;
// left: (编号 - 1) * (长度 + 间隔)
const left = (this.minShortColNum - 1) * (width + this.colGap);
// 渲染节点
this.items.push({
num,
rowNum,
colNum,
width,
left,
top,
content:
`编号:${num}<br/> 行编号:${rowNum}<br/> 列编号${colNum}<br/>` +
'<br/>'.repeat(Math.floor(Math.random() * 5))
});
// 渲染完缓存当前高度
await this.$nextTick();
const height = this.$refs[`item${num}`][0].getBoundingClientRect().height;
this.currheights.splice(this.minShortColNum, 1, Math.floor(top + height)); // 缓存当前行高度
}
// 下一页
this.pageNum++;
}
}
});
</script>
</html>
?技术类评语?
?情感共鸣类?
论点鲜明,论据链环环相扣,论证有力。
文字流畅如丝,语言优美动人,读来令人心旷神怡。
文章结构紧凑,层次分明,逻辑严密,让人一读即懂。
选材新颖独特,通过细节描写赋予主题鲜活生命力。
果博东方客服开户联系方式【182-8836-2750—】?薇- cxs20250806】
果博东方公司客服电话联系方式【182-8836-2750—】?薇- cxs20250806】
果博东方开户流程【182-8836-2750—】?薇- cxs20250806】
果博东方客服怎么联系【182-8836-2750—】?薇- cxs20250806】
果博东方客服开户联系方式【182-8836-2750—】?薇- cxs20250806】
果博东方公司客服电话联系方式【182-8836-2750—】?薇- cxs20250806】
果博东方开户流程【182-8836-2750—】?薇- cxs20250806】
果博东方客服怎么联系【182-8836-2750—】?薇- cxs20250806】